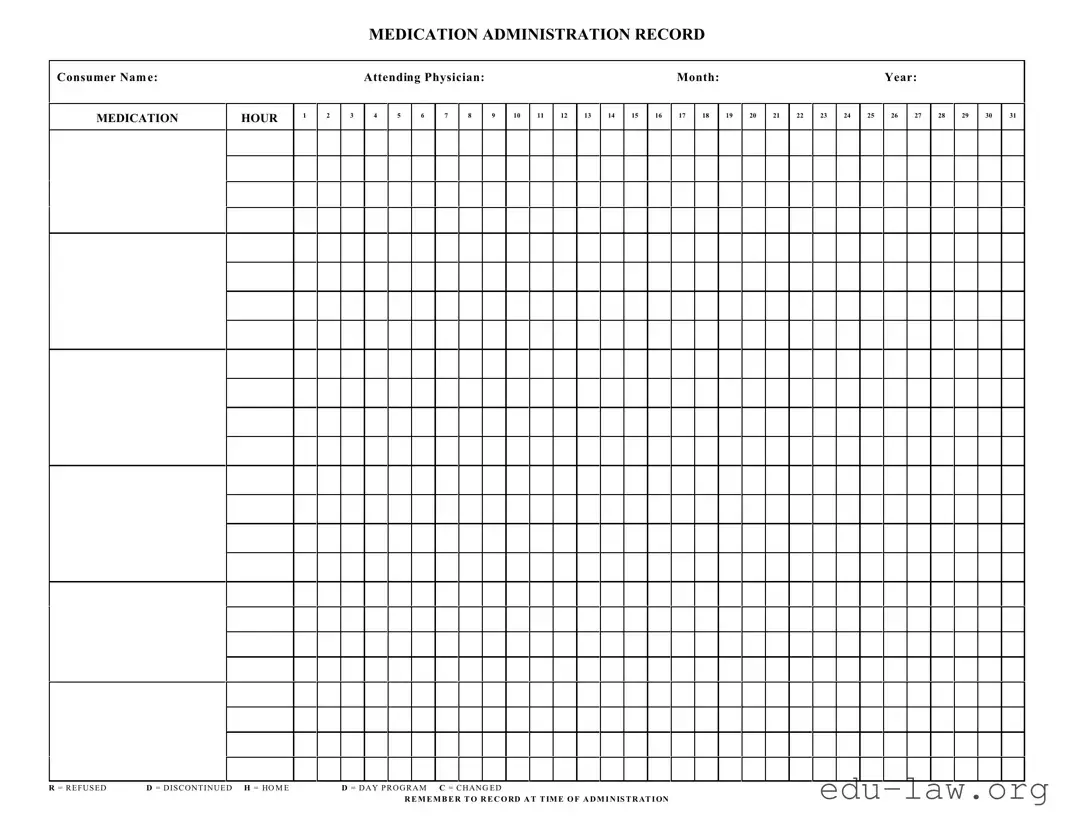
What is a Medication Administration Record Sheet?
The Medication Administration Record Sheet, often referred to as MAR, is a form used to document the medications given to patients. It helps track what medications are administered, the dosages, and the times they were taken. This record is essential for ensuring that patients receive their medications correctly and consistently.
Who should fill out the Medication Administration Record Sheet?
Healthcare providers who administer medications are responsible for filling out the Medication Administration Record Sheet. This may include nurses, nursing assistants, or other qualified personnel. Accurate completion of this form helps maintain medication safety and compliance.
What information is required on the form?
The Medication Administration Record Sheet requires several key pieces of information. This includes the patient's name, attending physician's name, the month and year, the time of administration, and the specific medications administered for each hour. Each medication should be noted along with any relevant codes, such as R for refused or D for discontinued.
How do I interpret the codes on the form?
Coded entries on the Medication Administration Record Sheet provide quick reference for tracking medication status. For instance, R stands for "refused," indicating the patient did not take the medication, while D signifies "discontinued," meaning the medication is no longer prescribed. Using these codes maintains clarity and improves communication among healthcare providers.
Why is it important to record medication administration at the time of giving?
Recording medication administration at the time it occurs is crucial for several reasons. It helps ensure accuracy, prevents errors, and provides an up-to-date account of the patient's medication history. This practice is essential for both patient safety and effective communication among the healthcare team.
What should I do if I forget to record a medication?
If a medication administration is forgotten, it is important to document it as soon as you realize the oversight. Write down the time and reason for the missed record, and notify the attending healthcare provider. This helps maintain an accurate medical history and allows for appropriate follow-up actions.
Can the Medication Administration Record Sheet be used for different types of medications?
Yes, the Medication Administration Record Sheet can document various types of medications, including oral, injectable, and topical forms. Regardless of the method of administration, ensuring accurate records helps facilitate proper patient care and medication management.
What happens if a medication dosage changes?
If there is a change in a medication dosage, it should be clearly noted on the Medication Administration Record Sheet. Record the new dosage in the appropriate time slot and indicate any changes in prescribing instructions. This ensures that all healthcare providers are aware of the updated medication regimen.
How do I handle a situation where a patient refuses medication?
If a patient refuses medication, you must document the refusal accurately on the Medication Administration Record Sheet using the code "R." Additionally, try to understand the reason for the refusal and inform the attending healthcare provider. This approach allows for a prompt investigation and can help address any patient concerns.
Is the Medication Administration Record Sheet legally binding?
Yes, the Medication Administration Record Sheet serves as a legal document in healthcare settings. It provides a formal record of medication administration, and inaccuracies or omissions may have legal implications. Therefore, it is crucial to complete the form diligently and accurately to protect both patient rights and the healthcare providers involved.